Hosting Your Web Application¶
Great! You've built your web app and have it running locally on 127.0.0.1 (your machine).
But what if you want to share your creation with the world?
That’s where deployment comes in.
There are methods to host your app locally, and allow people to connect to your server (your machine) directly to access your web application. There are broadly two methods for hosting your app on the internet:
Self hosting¶
This is what a few companies actually do, they have a dedicated machine to act as the server for their application, and requires quite a bit of setup and resources for it to work decently.
Cloud hosting¶
You know how in self hosting you had to dedicate your machine just for running as the application server?
Well, what if someone gives one to you, so you don't have to dedicate your own resources, for a small price of course. Maybe over the internet, so you are not really getting a physical machine so to speak, but an access to use a physical machine that is connected to the internet.
Well, that's the entire concept of a Virtual Machine, and Cloud Hosting in a nutshell.
And this is also the entire business concept of AWS, Microsoft Azure, GCP, and many others. These are called Web Hosting Services
Much simper to host static websites rather than dynamic websites using servers.
A little bit about the internet¶
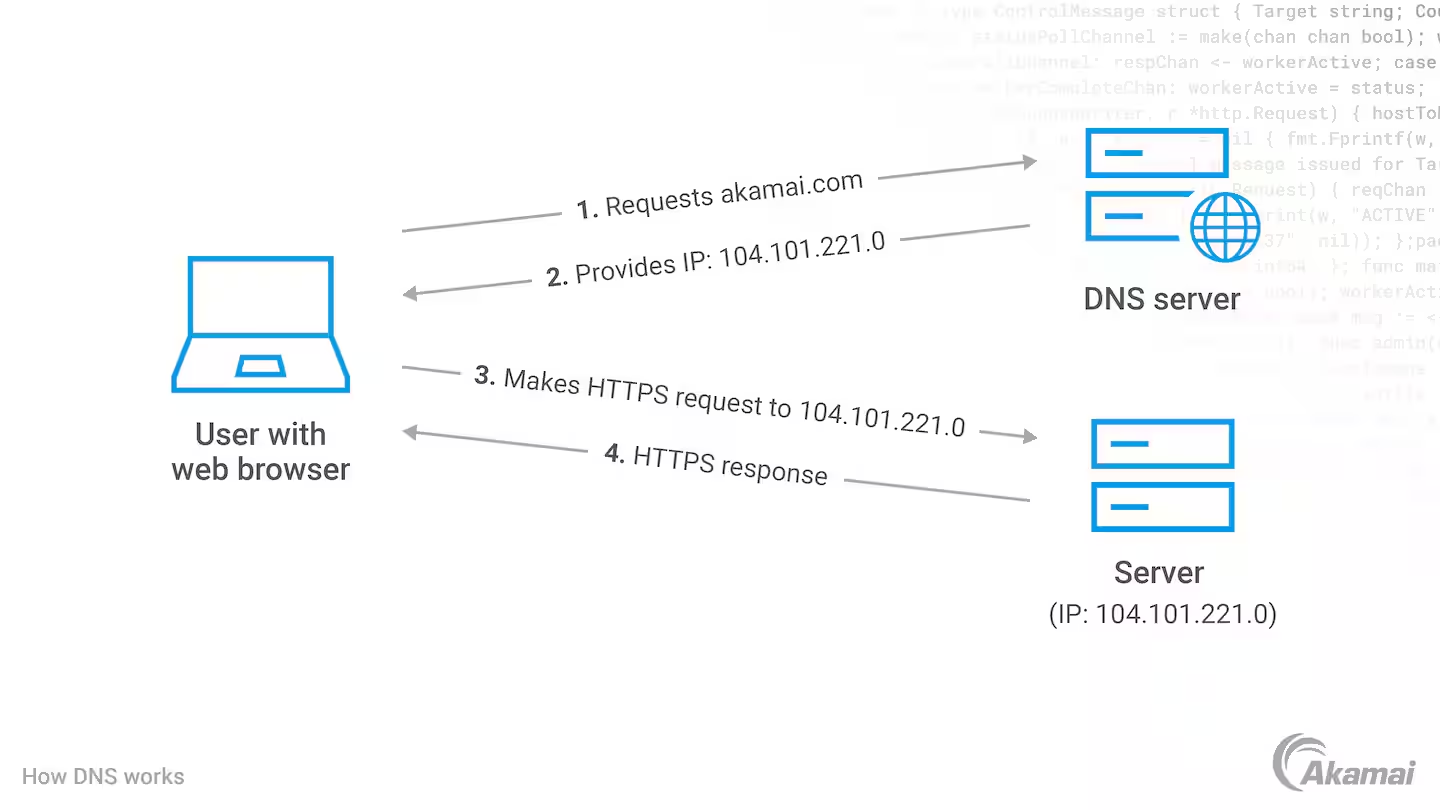
You'll need to have an idea of the following terms, just to get the overall picture:
-
IP Address
-
Domain
-
Sub Domain
-
DNS
There's a whole bunch of other 100+ things involved, but to get you started, just the concept of these 4 should be enough.
Now, a few web hosting services actually have a free tier, where they usually give you access to their resources to use as a web server, and a domain for you to access your web app, so you don't have to painfully type out the server ip address to access it.
A few free hosting services (with free tier):**¶
We'll be using PythonAnywhere: A free to use web hosting service to host our web app.