A Full Stack Portfolio Website¶
In this workshop, we'll be building a simple portfolio website with Flask and a MySQL database. We'll cover everything from setup to integrating the database and creating a user-friendly front end with Bootstrap.
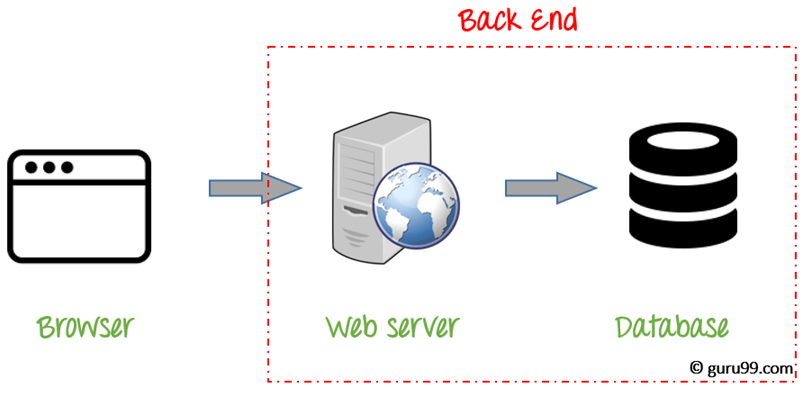
Introduction to Front-End and Back-End¶
Before diving into building the project, it's crucial to understand the foundational concepts of web development:
- Front-End (Client-Side): This is the part of the application that users interact with directly. It includes everything a user experiences on the browser, such as HTML (structure), CSS (styling), and JavaScript (functionality).
- Back-End (Server-Side): This is the behind-the-scenes functionality of the application. It handles data processing, server communication, database management, and more. Back-end code is run on the server and interacts with the front-end via HTTP methods like GET (fetch data) and POST (send data).
- Full Stack Development: This refers to working on both the front-end and back-end, providing a complete, well-rounded skill set for building web applications.
Prerequisites¶
-
Python installed (version 3.7+ recommended)
-
Download A Nice Blue Mountain
1. Project Setup¶
1.1 Setting up a Virtual Environment¶
To ensure we have an isolated workspace, let's create and activate a virtual environment. Open CMD and type
python3 -m venv myenv
after this we can activate our environment by typing out
myenv\Scripts\activate <for windows>
OR
source myenv/bin/activate <for Mac/Linux>
1.2 Installing Flask and Dependencies¶
With the virtual environment activated, install Flask and other dependencies.
pip install Flask
pip install Flask-SQLAlchemy
2. Building the Basic Front-End Layout¶
To start, we will focus on building the initial structure of the front-end using HTML and CSS. This section will guide you through understanding the provided index.html and style.css files.
portfolio/
├── app/
│ ├── templates/
│ │ └── index.html
│ └── static/
│ └── css/
│ └── style.css
├── run.py
run.py: This will initialize and run the Flask app.
from flask import Flask, render_template
# Initialize the Flask app
app = Flask(__name__, static_folder='app/static', template_folder='app/templates')
# Route for the homepage
@app.route('/')
def index():
return render_template('index.html')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
Let us start of by creating the index.html for our portfolio website followed by the style.css and run the app to see what we have
The HTML File (index.html)¶
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>My Portfolio</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{{ url_for('static', filename='css/style.css') }}">
</head>
<body>
<!-- Header with Navigation Links -->
<header class="header">
<a href="#home" class="logo">My Portfolio</a>
<nav class="nav-links">
<a href="#home">Home</a>
<a href="#about">About Me</a>
</nav>
</header>
<!-- Home Section -->
<section id="home" class="section red-section">
<div class="content">
<h1 class="main-text">Mustafa Fatehi</h1>
<p>Welcome to my personal portfolio!</p>
</div>
</section>
<!-- About Section -->
<section id="about" class="section white-section">
<div class="content">
<h1>About Me</h1>
<p>Hello! I'm Mustafa, a web developer experienced in Flask, Python, and front-end technologies.</p>
</div>
</section>
</body>
</html>
Explanation of the HTML Structure¶
<!DOCTYPE html>: Declares the document type and version of HTML (HTML5 in this case).<html lang="en">: The root element of the HTML document, withlang="en"specifying the language as English.<head>: Contains meta-information about the document, such as character encoding, viewport settings for responsive design, title, and linked resources (like CSS).<link rel="stylesheet">: Links to thestyle.cssfile usingurl_for()to serve the static file.<body>: Contains the main content of the web page.<header>: A container for introductory content and navigation links.<a>: An anchor element used for navigation; it can link to sections within the page or external pages.<section>: Defines sections in a document, used to group thematic content.<div>: A generic container element that can be used to group content for styling or layout purposes.<h1>and<p>: Header and paragraph tags, respectively, used for headings and regular text.
Detailed Explanation of the Header Section¶
<header class="header">
<a href="#home" class="logo">My Portfolio</a>
<nav class="nav-links">
<a href="#home">Home</a>
<a href="#about">About Me</a>
</nav>
</header>
1. <header class="header">:¶
- The
<header>element is used to group introductory content, navigation links, or other elements that appear at the beginning of a web page or a section. - The
class="header"assigns a CSS class to the<header>element, allowing it to be styled specifically through the CSS rules associated with.header.
2. <a href="#home" class="logo">My Portfolio</a>:¶
<a>(Anchor tag): This tag is used for hyperlinks. It can navigate to another page, a different section within the same page, or an external site.href="#home": Thehrefattribute sets the link's destination. In this case,#homeis an internal link that points to an element with theid="home"on the same page, facilitating smooth scrolling navigation.class="logo": This assigns a CSS classlogoto the anchor tag, which can be styled separately to create a distinct appearance (e.g., different font size or color).- Content ("My Portfolio"): This is the clickable text displayed as the link, often styled prominently to act as a branding or main title link.
3. <nav class="nav-links">:¶
- The
<nav>element is a semantic HTML5 tag that represents a section of the page intended for navigation links. It helps screen readers and search engines understand that the contained links are for navigating the site. class="nav-links": This class allows specific CSS styling to be applied to the entire<nav>block or individual child elements within it.
4. Navigation Links (<a> elements inside <nav>):¶
<a href="#home">Home</a>and<a href="#about">About Me</a>: These are the anchor tags within the<nav>element that act as clickable navigation items.href="#home"andhref="#about"specify that these links will scroll to the elements withid="home"andid="about"on the current page.- The visible text ("Home" and "About Me") is what users will see and click on.
The CSS File (style.css)¶
body {
font-family: 'Arial', sans-serif;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.header {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
padding: 1rem;
background-color: #333;
color: #fff;
}
.header .logo {
font-size: 1.5rem;
text-decoration: none;
color: #fff;
}
.header .nav-links a {
margin-left: 1rem;
text-decoration: none;
color: #fff;
}
.section {
padding: 2rem;
text-align: center;
}
.red-section {
background-color: #f44336;
color: #fff;
}
.white-section {
background-color: #fff;
color: #333;
}
.content h1 {
margin-bottom: 1rem;
font-size: 2.5rem;
}
.content p {
font-size: 1.2rem;
}
Explanation of the CSS File¶
body: Defines the base styles for the entire document, setting the font family and removing default margins and padding for a clean slate..header: Targets the<header>element. Thedisplay: flexproperty allows items inside to be aligned horizontally, withjustify-content: space-betweendistributing them evenly andalign-items: centeraligning them vertically.- Color Properties:
background-color: #333: Sets the background color to a dark shade (for the header).color: #fff: Sets the text color to white.- Class Selectors:
.logoand.nav-links a: Custom styling for elements within the header, specifying text properties like color and margin..section: Applies padding and center-alignment to all sections..red-sectionand.white-section: Adds specific background colors and text colors to thehomeandaboutsections for visual differentiation.- Nested Selectors:
.header .nav-links a: This ensures only anchor tags within.nav-linksreceive specific styling.- Typography:
h1andpstyles: Adjustments for heading and paragraph elements within.contentto enhance readability and spacing.
How CSS Selectors Work¶
- Class Selector (
.header): Targets elements with the classheader. - Descendant Selector (
.header .logo): Selects elements with the classlogothat are descendants of.header. - Element Selector (
h1,p): Targets<h1>and<p>elements directly, applying specified styles to them.
How the CSS Applies to HTML Elements¶
CSS is applied based on selectors that match the HTML elements:
- For example,
.headerinstyle.cssmatches<header class="header">inindex.html, applying all the specified properties to that element. - Nested rules, like
.header .nav-links a, style anchor tags only when they are within the.nav-linksclass inside.header.
Once you run the flask app again , this time you will see a much better looking setup comapred to before , we now have color coded the sections and overall it looks like there is some structure to it but there can be a lot of work done so let us make this look a bit more aesthetic.¶
Refer to the Bootstrap Documentation
Let's start of by making a few changes to our index.html¶
- Changing the fonts : you can add these lines at the start to custom import the font and the bootstrap element for styling
.
.
.
<title>My Portfolio</title>
<!-- Link to Bootstrap for base styling -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.5.3/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-TX8t27EcRE3e/ihU7zmQxVncDAy5uIKz4rEkgIXeMed4M0jlfIDPvg6uqKI2xXr2" crossorigin="anonymous">
<!-- Custom font -->
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Orbitron:wght@500&display=swap" rel="stylesheet"><!-- Custom CSS -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{{ url_for('static', filename='css/style.css') }}">
.
.
.
- Adding a Contact section : We can add one more section called contact section as such hyper referencing the links to our socials for faster understanding , add this after the
white-section
<section id="contact" class="contact-section">
<div class="content">
<h2>Contact</h2>
<p>Phone: <a href="tel:+1234567890">+1234567890</a></p>
<p>Email: <a href="mailto:your.email@example.com">your.email@example.com</a></p>
<div class="social-links">
<a href="https://linkedin.com/in/yourusername" target="_blank">LinkedIn</a>
<span> | </span>
<a href="https://instagram.com/yourusername" target="_blank">Instagram</a>
</div>
</div>
</section>
After all these changes our current index.html should look like
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>My Portfolio</title>
<!-- Link to Bootstrap for base styling -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.5.3/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-TX8t27EcRE3e/ihU7zmQxVncDAy5uIKz4rEkgIXeMed4M0jlfIDPvg6uqKI2xXr2" crossorigin="anonymous">
<!-- Custom font -->
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Orbitron:wght@500&display=swap" rel="stylesheet">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{{ url_for('static', filename='css/style.css') }}">
</head>
<body>
<header class="header">
<a href="#home" class="logo">My Portfolio</a>
<nav class="nav-links">
<a href="#home">Home</a>
<a href="#about">About Me</a>
<a href="#contact">Contact</a>
</nav>
</header>
<main>
<section id="home" class="section red-section">
<div class="content">
<h1 class="main-text">Mustafa Fatehi</h1>
<p>Welcome to my portfolio! I am excited to share my work with you.</p>
</div>
</section>
<section id="about" class="section white-section">
<div class="content">
<h1>About Me</h1>
<p>Hello! I'm Mustafa, a web developer experienced in Flask, Python, and front-end technologies. I create responsive, user-friendly web applications.</p>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Contact Section -->
<section id="contact" class="contact-section">
<div class="content">
<h2>Contact</h2>
<p>Phone: <a href="tel:+1234567890">+1234567890</a></p>
<p>Email: <a href="mailto:your.email@example.com">your.email@example.com</a></p>
<div class="social-links">
<a href="https://linkedin.com/in/yourusername" target="_blank">LinkedIn</a>
<span> | </span>
<a href="https://instagram.com/yourusername" target="_blank">Instagram</a>
</div>
</div>
</section>
</main>
</body>
</html>
Explanation of New HTML Elements and Attributes¶
-
Font and Bootstrap Import (
<link>Tags): -
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Orbitron:wght@500&display=swap" rel="stylesheet">:- This
<link>element imports a custom Google Font, "Orbitron," which is applied to the entire page. It provides a unique and modern typeface that enhances the design. - The
wght@500specifies the font weight (in this case, medium/bold).
- This
-
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.5.3/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-TX8t27EcRE3e/ihU7zmQxVncDAy5uIKz4rEkgIXeMed4M0jlfIDPvg6uqKI2xXr2" crossorigin="anonymous">:- This link includes the Bootstrap CSS framework. It provides base styling, grid layouts, and utility classes that simplify styling and layout processes.
-
<section id="contact" class="contact-section">: -
The
id="contact"attribute allows internal navigation (e.g., clicking a link in the nav bar withhref="#contact"will scroll to this section). -
The
class="contact-section"allows this specific section to be styled independently with targeted CSS. -
Hyperlinked Contact Information:
-
<a href="tel:+1234567890">+1234567890</a>:- This
tel:protocol in thehrefattribute creates a clickable link that opens the phone dialer on mobile devices.
- This
<a href="mailto:your.email@example.com">your.email@example.com</a>:- The
mailto:protocol creates a link that opens the user’s default email client to compose a new message.
- The
target="_blank"on social links:- Opens the linked page in a new browser tab, which keeps the portfolio page open when users visit external sites.
Let us now make changes to our style.css according to the changes we made in the index.html¶
/* Reset and Default Styles */
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
html, body {
scroll-behavior: smooth;
font-family: 'Orbitron', sans-serif;
overflow-x: hidden;
}
body {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
/* Header */
.header {
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
padding: 10px 20px;
font-size: 1rem;
color: #ffffff;
background-color: #1b263b;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
width: 100%;
z-index: 1000;
}
.logo {
font-weight: bold;
text-decoration: none;
color: #ffffff;
}
.nav-links a {
text-decoration: none;
color: #ffffff;
margin-left: 15px;
}
.nav-links a:hover {
color: #a9d6e5;
}
/* Section Styling */
.section {
min-height: 100vh;
padding-top: 80px; /* Adjusted for fixed header */
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
text-align: center;
}
.content {
max-width: 600px;
}
/* Section Background Colors */
.red-section {
background-color: #d90429;
color: #ffffff;
}
.white-section {
background-color: #ffffff;
color: #121212;
}
.contact-section {
background-color: #f0f0f0;
color: #333;
padding: 40px 20px;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
flex-direction: column;
text-align: center;
}
.social-links a {
font-weight: bold;
color: #007bff;
margin: 0 10px;
}
.social-links a:hover {
text-decoration: underline;
}
Explanation of New CSS Elements¶
-
Smooth Scroll Behavior (
scroll-behavior: smooth): -
scroll-behavior: smooth;in thehtml, bodyselector makes scrolling between sections smooth when users click internal navigation links. This enhances the user experience by providing a polished transition effect. -
Overflow Property (
overflow-x: hidden): -
overflow-x: hidden;ensures there is no horizontal scrollbar, preventing accidental sideways scrolling and keeping the layout clean. -
Header Padding (
padding: 10px 20px): -
This adds vertical (10px) and horizontal (20px) padding within the header, creating space inside and preventing the text and links from touching the edges.
-
Hover Effects (
:hover): -
.nav-links a:hoverand.social-links a:hover:- Changes the color or style when the user hovers over these links. This feedback indicates that the text is interactive.
text-decoration: underline;adds an underline to the link on hover for better visual feedback.
-
Fixed Header Adjustment (
padding-top: 80px;): -
The
.sectionclass haspadding-top: 80px;to prevent content from being hidden behind the fixed header. This pushes the content down, ensuring it is fully visible. -
Background Colors and Text Colors:
-
.contact-sectionhas a light background color (#f0f0f0) to differentiate it from other sections. -
The color contrast (
color: #333;) ensures text remains readable against the background. -
Flex Layout for Content:
-
.contact-sectionand.social-linksusedisplay: flexwithflex-direction: columnorrowto align items neatly and center-align them for better presentation. -
Aesthetic Enhancements:
-
.social-links a { font-weight: bold; }ensures social media links appear more prominent. - Color (
color: #007bff;) on social links adds a visually appealing shade of blue that stands out against the background.
After this when we run the run.py file , we can see this looks way better than before , but i think we are lacking on an integral part , that being that background looks too plain so let us add an a background image to make it look better
Adding an Image background¶
This is very simple and the only things we require are a background image we like and a few changes to our existing CSS code. I have chosen a file called blue_mountain.jpg as my background but you all are free to choose your own backgrounds
Firstly the file structure should now look like this
portfolio/
├── app/
│ ├── templates/
│ │ └── index.html
│ └── static/
│ ├── css/
│ │ └── style.css
│ ├── images/
│ │ └── blue_mountain.jpg
├── run.py
Common Mistakes to Avoid:¶
- Absolute Paths: Avoid using paths like
C:\...as they won't work in a web environment , Use relative path instead. - File Location: Double-check that
blue_mountain.jpgis indeed in theapp/static/imagesfolder.
Next we will change the red-section in the style.css
.red-section {
background-image: url('../images/blue_mountain.jpg');
background-size: cover;
background-position: center;
background-repeat: no-repeat;
color: #121212;
}
And that is it , you now have an image as your background . You can accordingly change the color of the fonts so that it matches the background image and style accordingly . Let us now move onto the BACKEND
3. Database Structure and Setup¶
1. What is a Backend?¶
The backend is the part of a website that users don’t see. It handles data, processes requests, and runs on a server. It’s like the kitchen in a restaurant where food is prepared – essential but hidden from customers.
2. What are Tables in a Database?¶
A database stores information in an organized way. Tables are like spreadsheets with columns (e.g., Name, Age) and rows (individual entries). Each table holds data about a specific topic, such as users or products.

3. What is SQL?¶
SQL (Structured Query Language) is used to manage and interact with data in databases. It lets you add, retrieve, update, and delete data. It’s simple to learn and powerful for handling data.
4. How Can We Get SQL?¶
You need a database management system (DBMS) to use SQL. Popular options include:
- MySQL: Open-source and widely used.
- SQLite: Lightweight and easy to use.
- PostgreSQL: Reliable and feature-rich.
3.1 Creating the Database for the Portfolio Project¶
In this section, we will create a SQLite database to store and manage user comments for the portfolio website. This involves using Python's sqlite3 module to handle the database connection and execute SQL commands.
-
comments.db: -
This sqlite3 database file created automatically.
We would like to create a table of this format:
CREATE TABLE comments (
ID INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
NAME VARCHAR(50),
POSITION VARCHAR(50),
COMMENT TEXT
);
Let us connect the database to the app , we can do this by adding these 2 lines to the run.py
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'sqlite:///comments.db'
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS'] = False
-
SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI: Points to a SQLite database file calledcomments.db. If this file doesn't exist, it will be created. -
SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS: Set toFalseto disable tracking changes to improve performance.
What is ORM?¶
Let's walk through how you would handle database operations without ORM (using raw SQL queries) versus with ORM (using SQLAlchemy), and why ORM is often preferred.
Without ORM: Using Raw SQL Queries¶
When you don't use an ORM, you need to manually write SQL queries for every interaction with the database. This approach requires a thorough understanding of SQL and the structure of your database. Here’s how the Comment table operations would look with raw SQL in Python
Inserting a New Record (RAW SQL)¶
conn = sqlite3.connect('comments.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Insert a new comment
name = "John Doe"
position = "Developer"
comment = "This is a raw SQL comment."
cursor.execute('''
INSERT INTO comments (name, position, comment)
VALUES (?, ?, ?)
''', (name, position, comment))
conn.commit()
conn.close()
Inserting a New Record (ORM)¶
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
class Comment(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
name = db.Column(db.String(80), nullable=False)
position = db.Column(db.String(120))
comment = db.Column(db.Text, nullable=False)
def __repr__(self):
return f"<Comment {self.name}>"
new_comment = Comment(name="John Doe", position="Developer", comment="This is an ORM comment.")
db.session.add(new_comment)
db.session.commit()
Advantages of Using ORM:¶
- Simpler Code: ORM reduces the amount of code you need to write. You interact with the database using Python syntax, which is more readable and maintainable.
- Security: SQLAlchemy automatically uses parameterized queries, which helps prevent SQL injection.
- Abstraction: You don't need to write SQL code for basic operations. The ORM handles the SQL generation, making code easier to read and understand.
- Relationships: ORM can easily define relationships between tables using Python, which is challenging and verbose with raw SQL.
- Portability: Switching databases is easier since SQLAlchemy abstracts the database backend. You can move from SQLite to PostgreSQL or MySQL with minimal changes.
- Debugging: Easier to debug due to higher-level error messages.
3.2 Creating a Form to accept and show comments¶
Before we move onto how we will connect these databases , we first need a way for the user to input their comments . This can be done using the <form> element in html .
Changes to the index.html¶
Add a new section to your index.html called comment-section which will have both the form and the carousel to display the comments . Let us take a look at the changes to be made.
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.1.slim.min.js" integrity="sha384-DfXdz2htPH0lsSSs5nCTpuj/zy4C+OGpamoFVy38MVBnE+IbbVYUew+OrCXaRkfj" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/popper.js@1.16.1/dist/umd/popper.min.js" integrity="sha384-9/reFTGAW83EW2RDu2S0VKaIzap3H66lZH81PoYlFhbGU+6BZp6G7niu735Sk7lN" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.5.3/dist/js/bootstrap.min.js" integrity="sha384-w1Q4orYjBQndcko6MimVbzY0tgp4pWB4lZ7lr30WKz0vr/aWKhXdBNmNb5D92v7s" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<!-- Comments Section -->
<section id="comments" class="section comments-section">
<div class="container">
<h2 class="text-center">Comments</h2>
<!-- Comment Form -->
<h3>Add a Comment</h3>
<form action="/add_comment" method="POST" class="comment-form">
<div class="form-group">
<input type="text" name="name" class="form-control" placeholder="Your Name" required>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<input type="text" name="position" class="form-control" placeholder="Your Position">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<textarea name="comment" class="form-control" placeholder="Your Comment" rows="3" required></textarea>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary btn-submit">Submit Comment</button>
</form>
</div>
</section>
Explanation of New Parts in index.html¶
Comment Form:
<form action="/add_comment" method="POST" class="comment-form">:- A form that sends user input to the
/add_commentroute via the POST method for handling submissions. <div class="form-group">:- A Bootstrap class that provides styling and spacing for form controls.
<input>and<textarea>:- Form elements for user input, styled using Bootstrap's
form-controlclass.
The Carousel¶
Now that puts the form in place but we also need a way to display the comments.this is where we bring in the carousel which we will place above the form
<!-- Carousel for Comments-->
<div id="commentCarousel" class="carousel slide" data-ride="carousel">
<div class="carousel-inner">
{% for comment in comments %}
<div class="carousel-item {% if loop.first %}active{% endif %}">
<div class="comment-box">
<strong>{{ comment['NAME'] }}</strong> ({{ comment['POSITION'] }}):
<p>{{ comment['COMMENT'] }}</p>
</div>
</div>
{% endfor %}
</div>
<a class="carousel-control-prev" href="#commentCarousel" role="button" data-slide="prev">
<span class="carousel-control-prev-icon" aria-hidden="true"></span>
<span class="sr-only">Previous</span>
</a>
<a class="carousel-control-next" href="#commentCarousel" role="button" data-slide="next">
<span class="carousel-control-next-icon" aria-hidden="true"></span>
<span class="sr-only">Next</span>
</a>
</div>
How Comments Are Loaded:¶
Backend Process:
In your Flask run.py file, there is a route that retrieves comments from the database and passes them to the template:
@app.route('/')
def index():
comments = Comment.query.all() # Retrieves all comments from the database
return render_template('index.html', comments=[{'NAME': c.name, 'POSITION': c.position, 'COMMENT': c.comment} for c in comments])
This route fetches all the records from the Comment table and converts them into dictionaries that are passed to the index.html template.
Now your index.html should look like this
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>My Portfolio</title>
<!-- Link to Bootstrap for base styling -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.5.3/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-TX8t27EcRE3e/ihU7zmQxVncDAy5uIKz4rEkgIXeMed4M0jlfIDPvg6uqKI2xXr2" crossorigin="anonymous">
<!-- Custom font -->
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Orbitron:wght@500&display=swap" rel="stylesheet">
<!-- Custom CSS -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="{{ url_for('static', filename='css/style.css') }}">
</head>
<body>
<!-- Header with Navigation Links -->
<header class="header">
<a href="#home" class="logo">My Portfolio</a>
<nav class="nav-links">
<a href="#home">Home</a>
<a href="#about">About Me</a>
<a href="#comments">Comments</a>
<a href="#contact">Contact</a>
</nav>
</header>
<!-- Main Sections -->
<main>
<!-- Home Section -->
<section id="home" class="section red-section">
<div class="content">
<h1 class="main-text">Mustafa Fatehi</h1>
<p>Welcome to my portfolio! I am excited to share my work with you.</p>
</div>
</section>
<!-- About Me Section -->
<section id="about" class="section white-section">
<div class="content">
<h1>About Me</h1>
<p>Hello! I'm Mustafa, a web developer experienced in Flask, Python, and front-end technologies. I create responsive, user-friendly web applications.</p>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Comments Section -->
<section id="comments" class="section comments-section">
<div class="container">
<h2 class="text-center">Comments</h2>
<!-- Carousel for Comments-->
<div id="commentCarousel" class="carousel slide" data-ride="carousel">
<div class="carousel-inner">
{% for comment in comments %}
<div class="carousel-item {% if loop.first %}active{% endif %}">
<div class="comment-box">
<strong>{{ comment['NAME'] }}</strong> ({{ comment['POSITION'] }}):
<p>{{ comment['COMMENT'] }}</p>
</div>
</div>
{% endfor %}
</div>
<a class="carousel-control-prev" href="#commentCarousel" role="button" data-slide="prev">
<span class="carousel-control-prev-icon" aria-hidden="true"></span>
<span class="sr-only">Previous</span>
</a>
<a class="carousel-control-next" href="#commentCarousel" role="button" data-slide="next">
<span class="carousel-control-next-icon" aria-hidden="true"></span>
<span class="sr-only">Next</span>
</a>
</div>
<!-- Comment Form -->
<h3>Add a Comment</h3>
<form action="/add_comment" method="POST" class="comment-form">
<div class="form-group">
<input type="text" name="name" class="form-control" placeholder="Your Name" required>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<input type="text" name="position" class="form-control" placeholder="Your Position">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<textarea name="comment" class="form-control" placeholder="Your Comment" rows="3" required></textarea>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary btn-submit">Submit Comment</button>
</form>
</div>
</section>
<!-- Contact Section -->
<section id="contact" class="contact-section">
<div class="content">
<h2>Contact</h2>
<p>Phone: <a href="tel:+1234567890">+1234567890</a></p>
<p>Email: <a href="mailto:your.email@example.com">your.email@example.com</a></p>
<div class="social-links">
<a href="https://linkedin.com/in/yourusername" target="_blank">LinkedIn</a>
<span> | </span>
<a href="https://instagram.com/yourusername" target="_blank">Instagram</a>
</div>
</div>
</section>
</main>
<!-- JavaScript for Carousel -->
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.5.1.slim.min.js" integrity="sha384-DfXdz2htPH0lsSSs5nCTpuj/zy4C+OGpamoFVy38MVBnE+IbbVYUew+OrCXaRkfj" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/popper.js@1.16.1/dist/umd/popper.min.js" integrity="sha384-9/reFTGAW83EW2RDu2S0VKaIzap3H66lZH81PoYlFhbGU+6BZp6G7niu735Sk7lN" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@4.5.3/dist/js/bootstrap.min.js" integrity="sha384-w1Q4orYjBQndcko6MimVbzY0tgp4pWB4lZ7lr30WKz0vr/aWKhXdBNmNb5D92v7s" crossorigin="anonymous"></script>
</body>
</html>
Now your run.py should look like this
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, redirect
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
app = Flask(__name__, static_folder='app/static', template_folder='app/templates')
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'sqlite:///comments.db'
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_TRACK_MODIFICATIONS'] = False
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
# Define the Comment model
class Comment(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.Integer, primary_key=True)
name = db.Column(db.String(80), nullable=False)
position = db.Column(db.String(120))
comment = db.Column(db.Text, nullable=False)
def __repr__(self):
return f"<Comment {self.name}>"
# Create the database tables (if not already created)
with app.app_context():
db.create_all()
@app.route('/')
def index():
comments = Comment.query.all()
return render_template('index.html', comments=[{'NAME': c.name, 'POSITION': c.position, 'COMMENT': c.comment} for c in comments])
@app.route('/add_comment', methods=['POST'])
def add_comment():
name = request.form['name']
position = request.form['position']
comment_text = request.form['comment']
new_comment = Comment(name=name, position=position, comment=comment_text)
db.session.add(new_comment)
db.session.commit()
return redirect('/')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
Now making changes to the style.css , add these to the style .css
/* Comments Section Styling */
.comments-section {
background-color: #302b2b;
padding: 40px 20px;
text-align: center;
}
.comments-section h2, .comments-section h3 {
margin-bottom: 20px;
color: #ffffff;
}
/* Carousel Styling */
.carousel {
width: 100%;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}
.carousel-inner {
max-width: 800px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.comment-box {
background-color: #494545; /* Dark gray background */
color: #ffffff; /* White text color */
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
font-size: 1.1rem;
text-align: left;
box-shadow: 0 4px 8px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1); /* Added shadow for depth */
}
/* Carousel Controls */
.carousel-control-prev, .carousel-control-next {
color: #ffffff;
}
.carousel-control-prev-icon,
.carousel-control-next-icon {
background-color: #ffffff; /* White icons */
border-radius: 50%;
}
/* Comment Form Styling */
.comment-form {
max-width: 600px;
margin: 0 auto;
padding: 20px; /* Padding for better spacing */
background-color: #383838; /* Background color for form */
border-radius: 10px; /* Rounded corners */
}
.comment-form .form-group {
margin-bottom: 15px;
}
.comment-form .form-control {
font-size: 1rem;
padding: 10px;
background-color: #494949; /* Darker input background */
color: #ffffff; /* White text color */
border: none; /* Removed default border */
border-radius: 5px; /* Rounded corners */
}
.comment-form .form-control::placeholder {
color: #b0b0b0; /* Lighter placeholder color */
}
.btn-submit {
background-color: #ff6b6b;
border: none;
color: #fff;
padding: 10px 20px;
font-size: 1rem;
cursor: pointer;
width: 100%;
border-radius: 5px; /* Rounded corners */
transition: background-color 0.3s; /* Smooth transition for hover */
}
.btn-submit:hover {
background-color: #ff8566;
}
4. Javascript Popup¶
This is just a small bit of javascript which will show a popup everytime a new comment is added.
<script>
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function() {
const form = document.querySelector('.comment-form');
form.addEventListener('submit', function(event) {
alert("Comment has been added!");
});
});
</script>
This script runs when the page is fully loaded:
-
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", function() { ... }): Ensures the code inside runs only after the DOM (web page) is fully loaded. -
const form = document.querySelector('.comment-form'): Selects the form element with the classcomment-form. -
form.addEventListener('submit', function(event) { ... }): Adds an event listener to the form that triggers when it is submitted. -
alert("Comment has been added!"): Displays an alert message saying "Comment has been added!" when the form is submitted.
5. Running the App¶
To run the flask app now , type the following command into the command shell and the site on http://127.0.0.1:5000
python run.py
Conclusion¶
In this project, we built a complete web application using Flask, showcasing the power of combining both front-end and back-end development to create a functional, interactive portfolio website. Here’s what we achieved step by step:
-
Understanding Front-End and Back-End:
-
We explored the roles of front-end (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) and back-end (Flask, Python) technologies in building web applications.
-
We discussed how HTTP methods like GET and POST allow communication between the front-end and back-end.
-
Building the Web Page:
-
We structured the main
index.htmlpage, including sections for displaying portfolio details, user comments, and contact information. -
We added styling with CSS and used Bootstrap for a responsive design, making the page look clean and professional.
-
Creating the Database:
-
We set up a SQLite database and created a
Commentmodel with SQLAlchemy to store user comments. -
We ensured the database could store, retrieve, and manage user input efficiently.
-
Developing the Comment Form and Display Carousel:
-
We integrated an input form that allows users to submit their comments and a Bootstrap carousel to display these comments dynamically.
-
Using Jinja2 templating, we looped through the list of comments from the database and rendered them on the page.
-
Adding JavaScript for User Feedback:
-
We added a simple JavaScript script that shows an alert to confirm when a comment is successfully submitted, enhancing user experience.
-
Connecting Front-End and Back-End:
-
The form submissions were linked to the Flask back-end, which processed the data, stored it in the database, and displayed it in the carousel.
- This demonstrated the seamless interaction between the front-end and back-end of a full-stack application.
